WAVE BL reimagined an application of asymmetric encryption and digital signatures for members of the supply chain to conduct paper-based global trade transactions digitally.
Unlocking the World of Encryption
They were the keys to our world, and there was no way in without them.
encryption: the process of converting information or data into a code, especially to prevent unauthorized access.

Symmetric Encryption: A Shared Secret
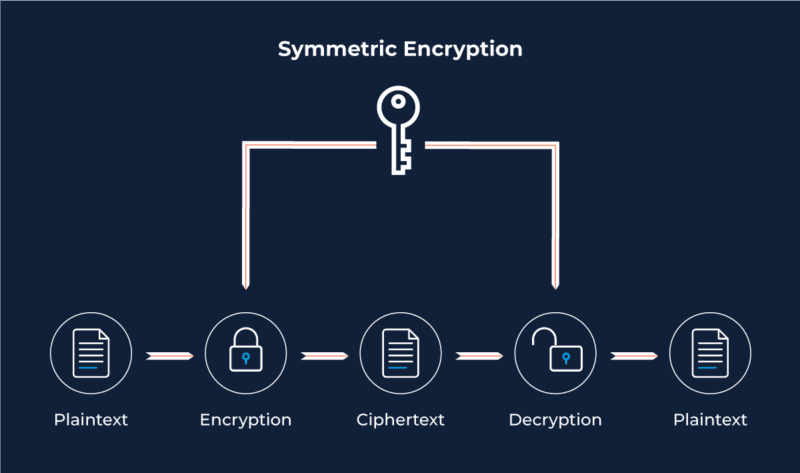
Asymmetric Encryption: A Stronger Form of Authentication
Using Asymmetric Encryption to transfer data
When using cryptographic keys to transfer data, we first need to identify the recipient of the message. The sender of the message will encrypt the document with the recipient’s Public Key. The recipient will then be able to read the message by decrypting the information with their Private Key.
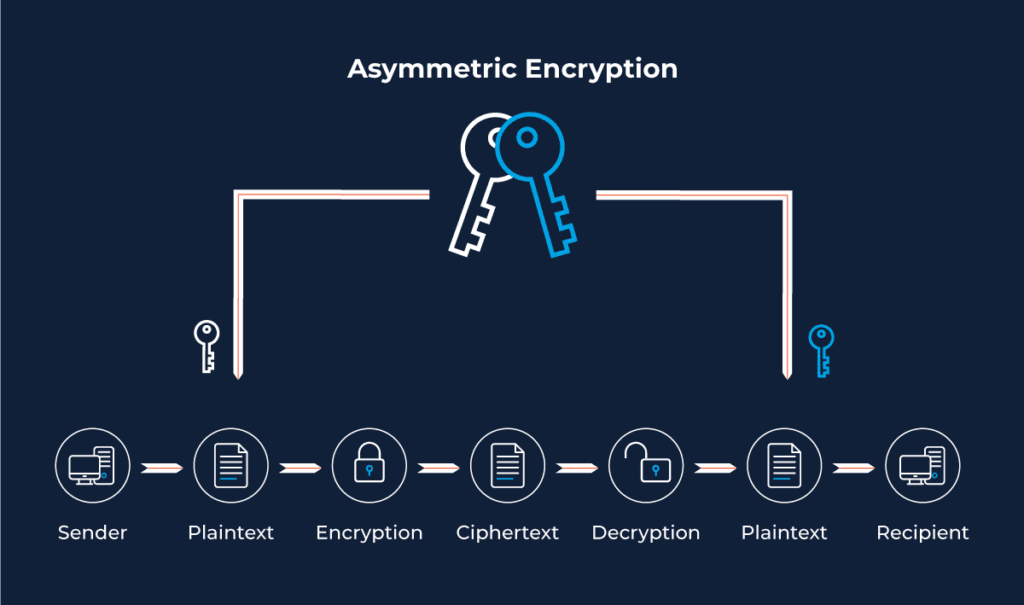
Using Asymmetric Encryption for Digital Signatures
The application of digital signatures ensures that the message being shared is free from data alterations and that the origination of the document and the sender’s identity is authentic.
The Drawbacks of Digital Signatures
- 1. Implementing in-house digital signatures: As beneficial as it is to have an added layer of security to a document; digital signatures can be cumbersome and costly. Users must first purchase a unique key pair, provided by the certificate authority (CA), apply dedicated software to sign data with the digital signatures, and validate the signatures of the data received. It is crucial to keep up to date with the algorithms and their advances — once a minor defect is detected, that algorithm is then void, and a different key pair must be used.
- 2. Lack of possession and time-stamp: Digital signatures verify authenticity and validity but do not manage any aspect of who possesses the document and when. The result is that several people can present the same digitally signed document, and there is no way to assess the valid possession holder.
Digital Signatures Reimagined with WAVE BL
- Distributed networks resolve the time-stamp and possession drawbacks mentioned above. Working in a distributed network enables a trust mechanism that makes it much harder for malicious actors to bypass a distributed system’s security with abnormal behavior in a real-time environment.WAVE BL reimagined an application of asymmetric encryption and digital signatures for members of the supply chain to conduct paper-based global trade transactions digitally. Tying distributed networks to digitally signed document distributions verifies the sole possessor of any given document
and validates the entire hand-off journey of the document accurately.
The ingenuity of our solution enables total confidentiality while working in fully transparent blockchain networks (a type of distributed network), utilizing asymmetric encryption. As a result, WAVE BL eliminates nearly any threat of document forgery and misinformation by embedding a significant security element of exchanging sensitive documents. The supply chain entities can collaborate seamlessly on a singular platform that preserves confidentiality and ensures the authenticity of any digital trade document and process associated with a shipment.
To learn more about the types of digital signatures we offer, download the PDF on WAVE BL digital signature.



